Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Definition The concept that the natural greenhouse effect has been enhanced by increased atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases (such as CO₂ and methane) emitted as a result of human activities These added greenhouse gases cause the earth to warm See greenhouse effectThe greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides

The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
Enhanced greenhouse effect definition
Enhanced greenhouse effect definition- Students struggle to express an expert understanding of greenhouse gases because they conflate the natural greenhouse effect and an enhanced greenhouse effect While many people understand that the greenhouse effect is natural, they may also associate greenhouse gases with global warming and, therefore, label these gases as badAn increase in temperature from greenhouse gases leading to increased water vapor (which is itself a greenhouse gas) causing further warming is a positive feedback, but not a runaway effect, on Earth Positive feedback effects are common (eg ice–albedo feedback) but runaway effects do not necessarily emerge from their presence



Untitled Document
Greenhouse effect is nothing but the process by which radiation from the planet's atmosphere warms up its surface to a temperature above the atmospheric level The thermal radiation from earth's surface is reabsorbed by greenhouse gases and redirected in all directionsThe problem is that our increased release of greenhouse gases is causing an increase in the greenhouse effect called the enhanced greenhouse effect This isA greenhouse is a structure, usually made of glass, in which temperature and humidity can be controlled for the cultivation or protection of plants A greenhouse is designed to trap heat from the sun's rays inside and acts to keep the plants inside warm, even when it is cold outside
warming of the surface and lower atmosphere of a planet (such as Earth or Venus) that is caused by conversion of solar radiation into heat in a process involving selective transmission of short wave solar radiation by the atmosphere, its absorption by the planet's surface, and reradiation as infrared which is absorbed and partly reradiated back to the surface by atmospheric gases Definition The concept that the natural greenhouse effect has been enhanced by anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases Increased concentrations of carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, CFCs, HFCs, PFCs, SF₆, NF₃, and other photochemically important gases caused by human activities such as fossil fuel consumption, trap more infraAlthough the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, there are concerns with something known as the enhanced greenhouse effectThe enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate changeThis effect refers to the increased heating of the Earth's surface as a result of a higher amount of greenhouse
Strengthening of the greenhouse effect through human activities is known as the enhanced (or anthropogenic) greenhouse effect This increase in radiative forcing from human activity has been observed directly and is attributable mainly to increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levelsEnhanced greenhouse effect The problem we now face is that human activities – particularly burning fossil fuels (coal, oil and natural gas), agriculture and land clearing – are increasing the concentrations of greenhouse gases This is the enhanced greenhouse effect, which is contributing to warming of the EarthDefine greenhouse effect greenhouse effect synonyms, greenhouse effect pronunciation, greenhouse effect translation, English dictionary definition of greenhouse effect greenhouse effect Energy radiated by the sun converts to heat when it reaches the earth Some heat is reflected back through the atmosphere, while some is




Details On Canvas Finals Review Ppt Download
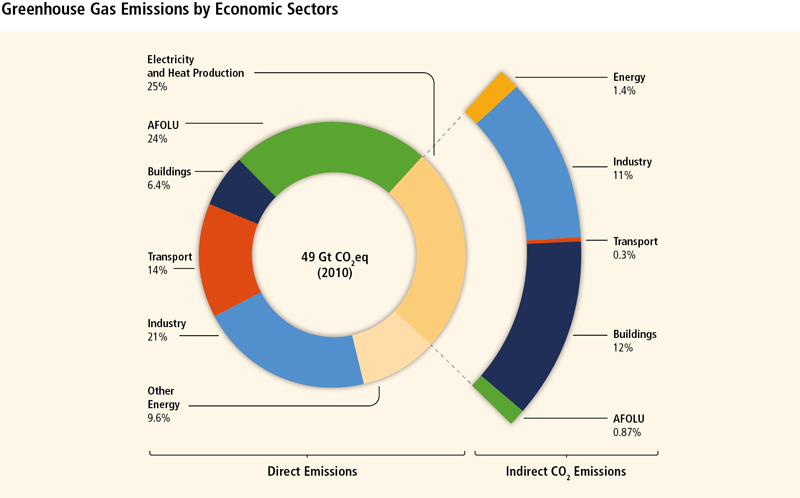



Causes Of Climate Change And Sea Level Rise Coastadapt
The concept that the natural greenhouse effect has been enhanced by anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases It is important to remember that the enhanced greenhouse effect is not the only factor acting on the climate system In the short term, the influence of greenhouse gases can be obscured by otherAnthropogenic or human release of carbon dioxide is what is contributing to an




Global Warming




Greenhouse Gases And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect greenhouse effect on Earth The greenhouse effect on EarthContrasts Enhanced greenhouse effect is due to human activity Greenhouse effect is a natural process Enhanced greenhouse effect = less energy escapes back into space & increases earth's temperature by 018⁰C every decade Enhanced greenhouse effect = levels of gases in atmosphere, especially CO2 have increased à'blanketThe greenhouse effect meaning 1 an increase in the amount of carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere (= mixture of Learn more




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



Stelr Org Au Wp Content Uploads 18 08 Greenhouseeffect E2 80 93naturalandenhanced Pdf
Furthermore, our findings suggest that the enhanced greenhouse effect from increased cloudiness and water vapor in the Arctic has highly likely inhibited the process of ice refreezing in winterHow the Greenhouse Effect Works Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is an atmospheric constituent that plays several vital roles in the environment It absorbs infrared radiation in the atmosphere It plays a crucial role in the weathering of rocks It is the raw material for photosynthesis and its carbon is incorporated into organic matter in the biosphereThe Greenhouse Effect Earth is much colder than the sun, but it is warmer than the space outside its atmosphere Earth's atmosphere is made up of gases, and
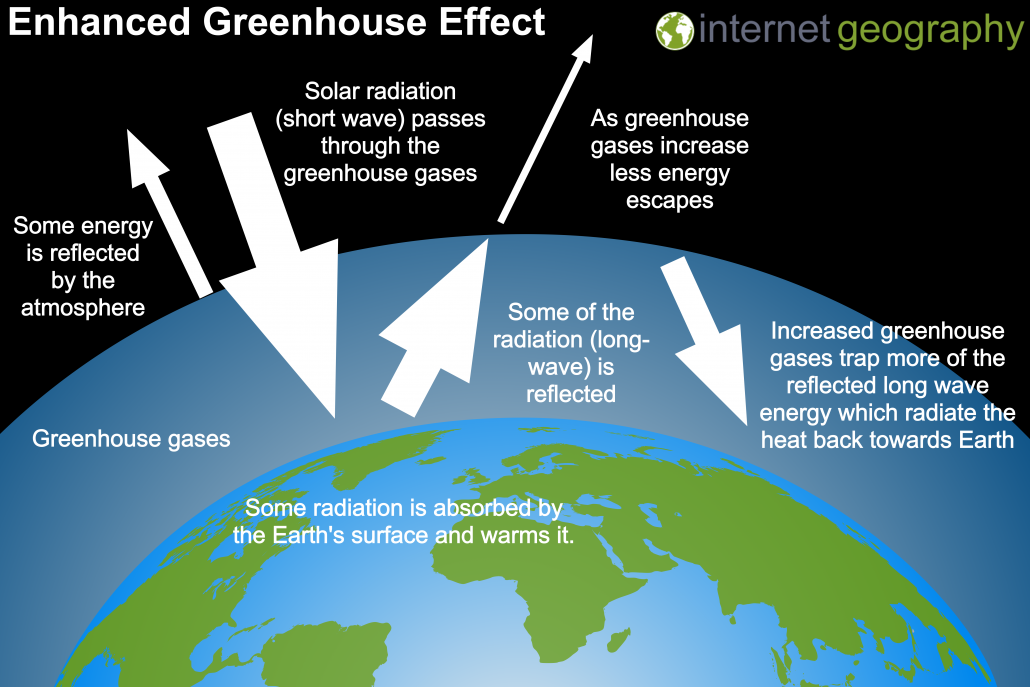



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography
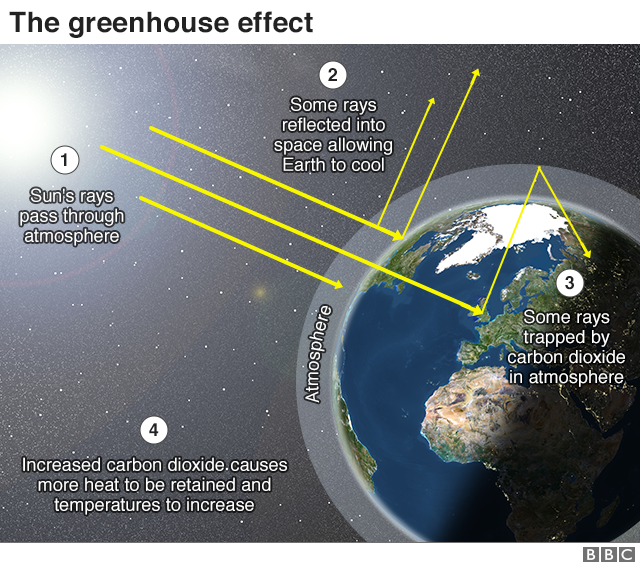



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News
Despite this subtle difference, we refer to this atmospheric process as the Greenhouse Effect and these gases as Greenhouse Gases because of their role in warming the Earth The Carbon Cycle Of the GHGs, CO 2 is of greatest concern because it contributes the most to the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect and climate change For this reason, scientists An enhanced greenhouse effect from CO2 has been confirmed by multiple lines of empirical evidence Satellite measurements of infrared spectra over the past 40 years observe less energy escaping to space at the wavelengths associated with CO2 Surface measurements find more downward infrared radiation warming the planet's surface This provides a direct, empirical The enhanced greenhouse effect and climate change The disruption to Earth's climate equilibrium caused by the increased concentrations of greenhouse gases has led to an increase in the global average surface temperatures This process is called the enhanced greenhouse effect
.png)



Greenhouse Effect Energy Education
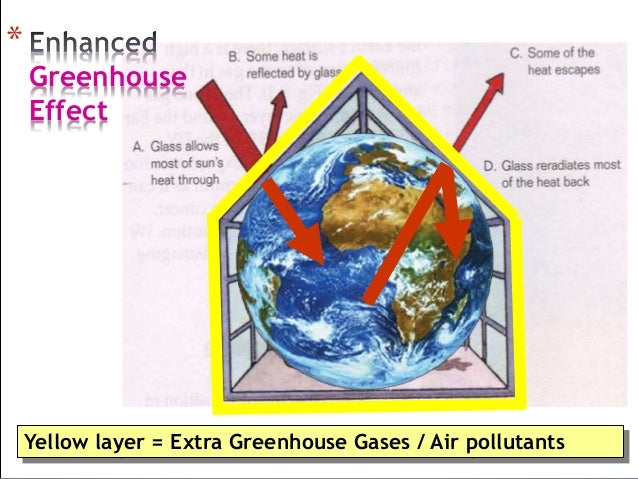



Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Definition Geography
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect the concept that the natural greenhouse effect has been enhanced by increased atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases (such as CO2 and methane) emitted as a result of human activitiesThe Greenhouse Effect and the Global Energy Budget Earlier, we noticed that if you do the energy balance calculation to figure out the temperature of our planet, it suggests that Earth should be 19 °C, which is 34 °C colder than the observed average global temperature of 15 °CThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works




Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme




Modern Atmosphere Time Scavengers
Currently, carbon dioxide accounts for more than 60 percent of the enhanced greenhouse effect caused by the increase of greenhouse gases, and the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is Greenhouse effect definition The greenhouse effect is the problem caused by increased quantities of gases such as Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examplesFind 52 ways to say GREENHOUSE EFFECT, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesauruscom, the world's most trusted free thesaurus




What Is An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Universe Today




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinatedCHAPTER 7 THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT We examine in this chapter the role played by atmospheric gases in controlling the temperature of the Earth The main source of heat to the Earth is solar energy, which is transmitted from the Sun to the Earth by radiation and is converted to heat at the Earth's surfaceThe greenhouse effect traps some of the energy from the Sun, which keeps our planet at a suitable temperature for life The problem is that our



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
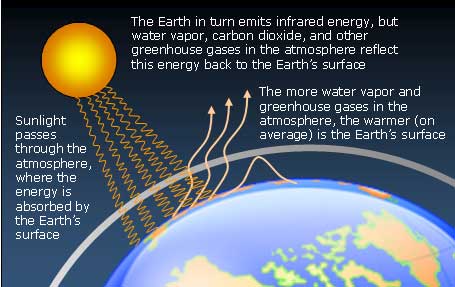



Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Warming Mrgeogwagg
A definition is something that represents an object or process, typically on a smaller scale In this case, the greenhouse effect that happens on our planet is far too large to see, so we recreate it smaller with visible results to help us understand this processGreenhouse gases let the sun's light shine onto the Earth's surface, but they trap the heat that reflects back up into the atmosphere In this way, they act like the insulating glass walls of a greenhouse The greenhouse effect keeps Earth's climate comfortable Without it, surface temperatures would be cooler by about 33 degrees Celsius An enhanced greenhouse effect from CO2 has been confirmed by multiple lines of empirical evidence Satellite measurements of infrared spectra over the past 40 years observe less energy escaping to space at the wavelengths associated with CO2 Surface measurements find more downward infrared radiation warming the planet's surface This provides a direct, empirical



Humans And The Greenhouse Effect Climate Institute




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica
Enhanced Greenhouse effect 'Greenhouse gases' are actually crucial to keeping our planet at a habitable temperature, without them the Earth would be about minus 17 degrees!The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence of



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Climate Change Science And Impacts Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Curious
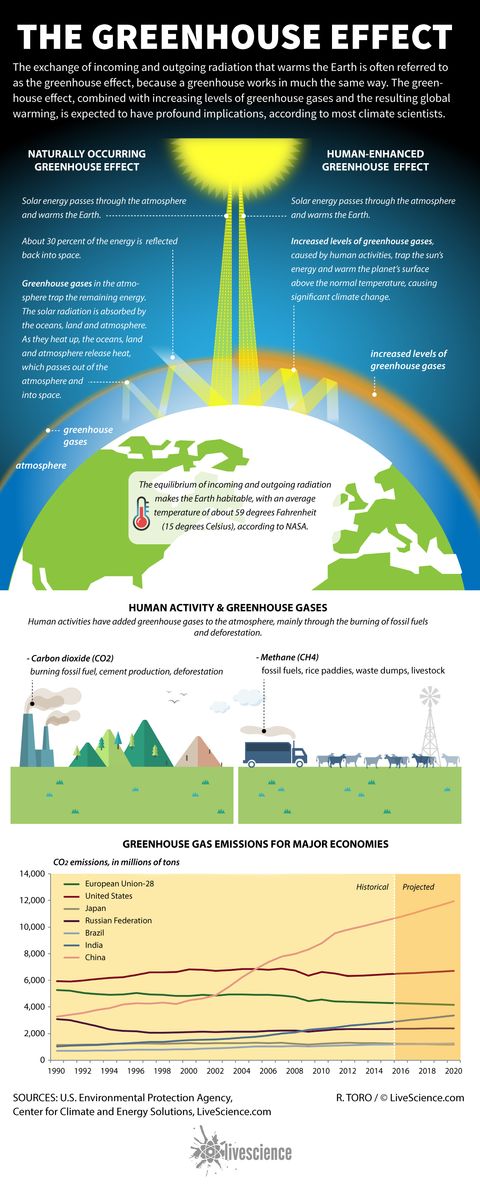



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Live Science




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Global Warming And Its Impacts In Pakistan Free Download Pdf




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect Is It Getting Warmer Definition Sun S Rays Are Trapped By Greenhouse Gases In Troposphere Heat Is Trapped Like A Greenhouse Ppt Powerpoint




Enhanced Greenhouse Effect On Global Warming Writework
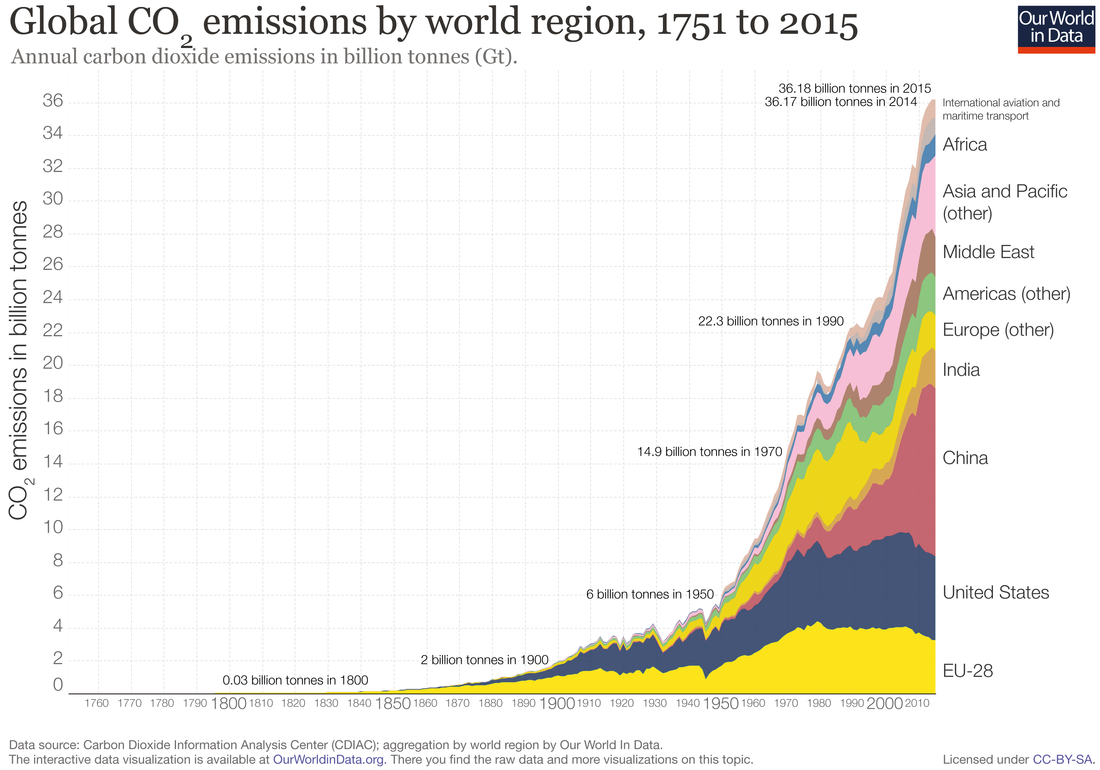



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geography Myp Gcse Dp
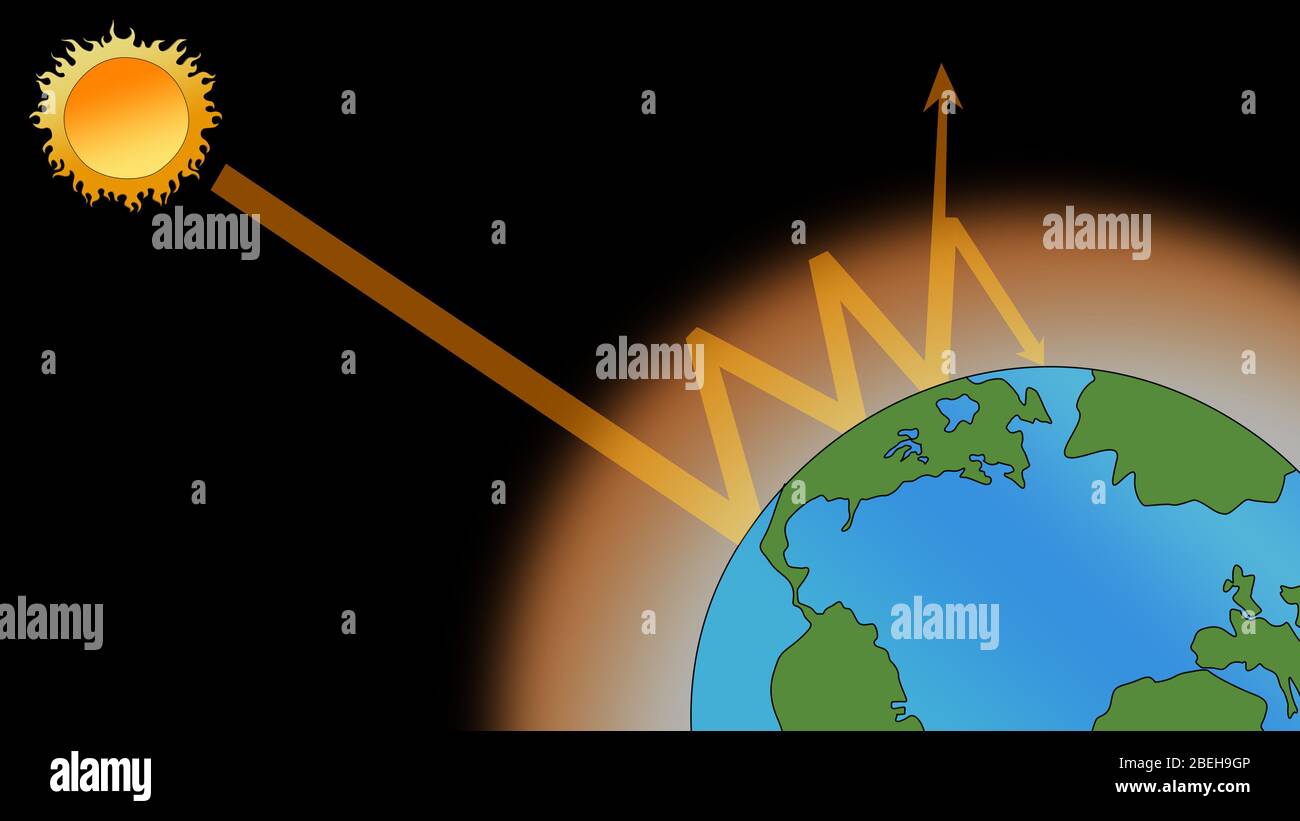



Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change



Team Braunschweig Project Content 14 Igem Org
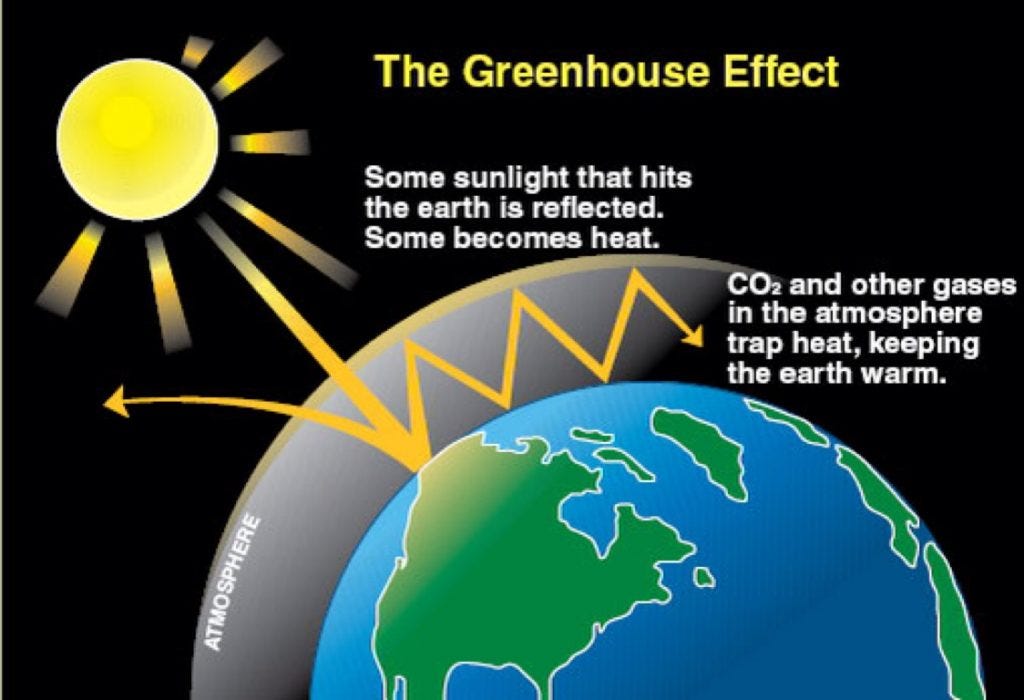



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium
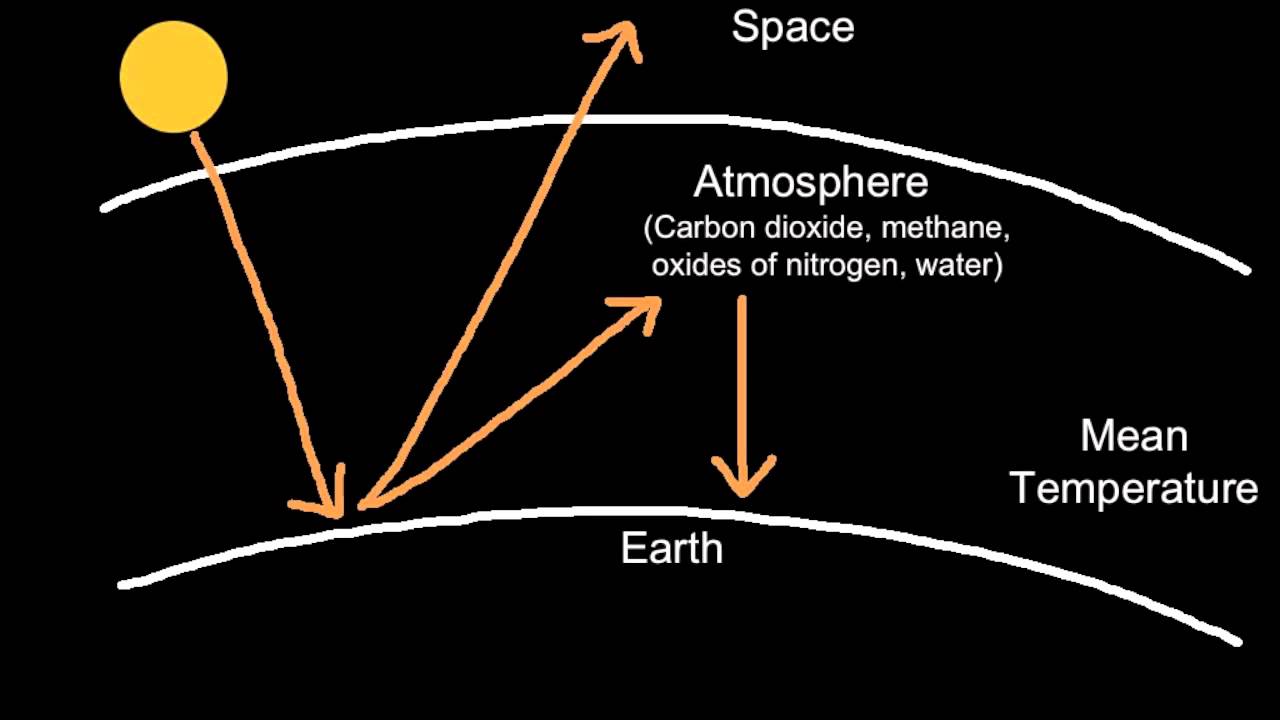



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube




A Natural Greenhouse Effect B Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram
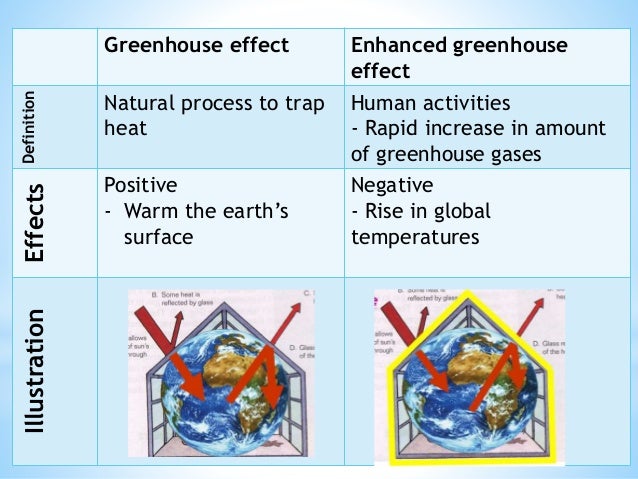



Topic 5




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geography Myp Gcse Dp



3



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com
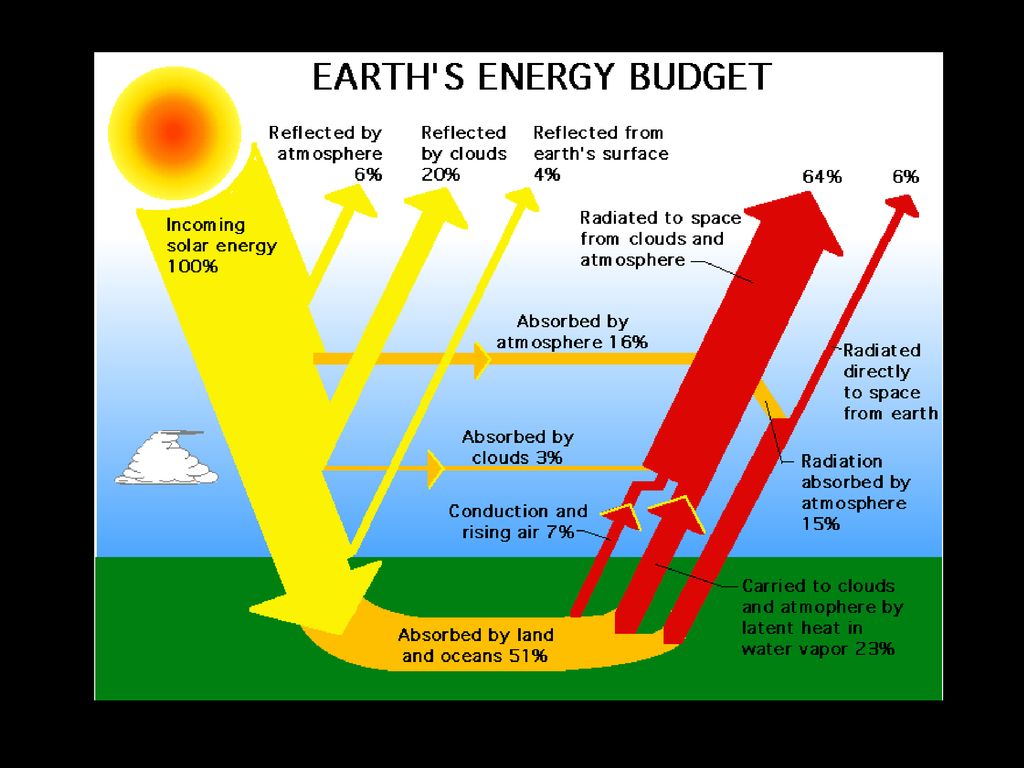



The Natural Greenhouse Effect And Anthropogenic Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Ppt Download



Global Climate Change And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect



Global Warming




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects
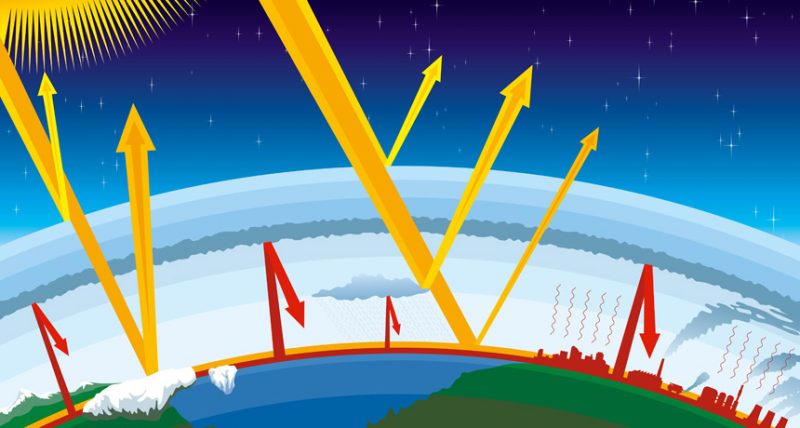




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
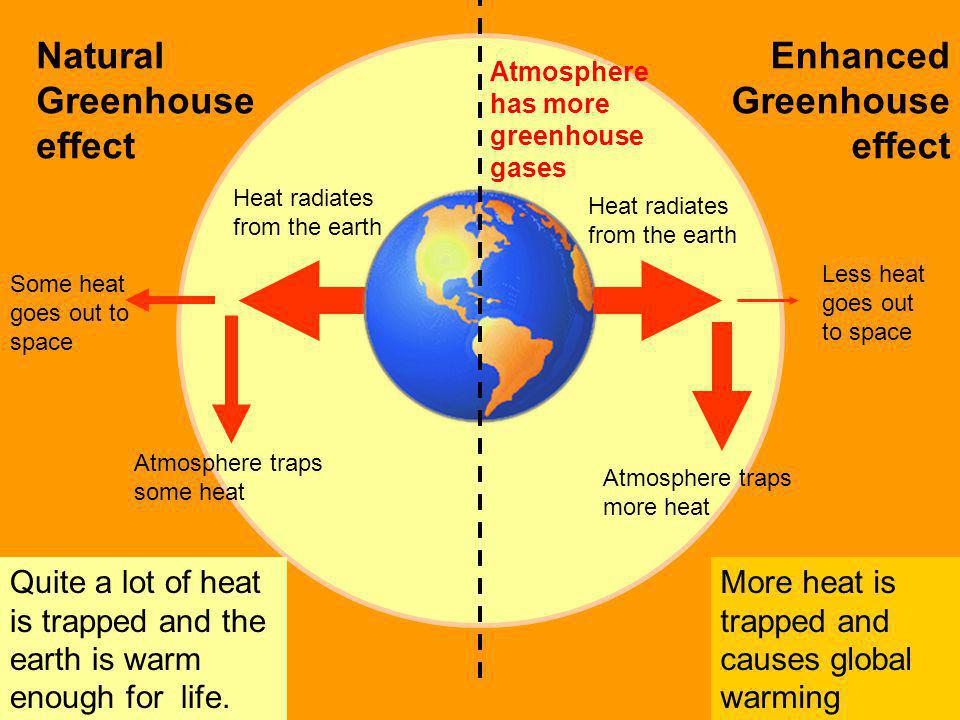



What Is Global Warming Ppt Video Online Download




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




6 3 The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Climate Change Organization
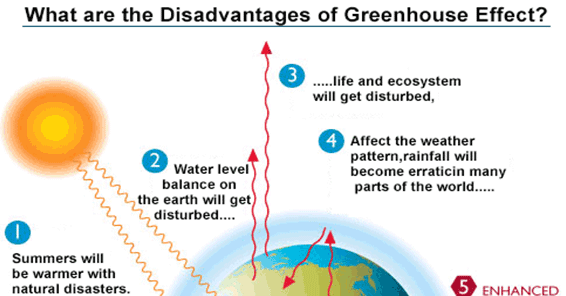



Disadvantages Of Greenhouse Effects Myassignmenthelp Com
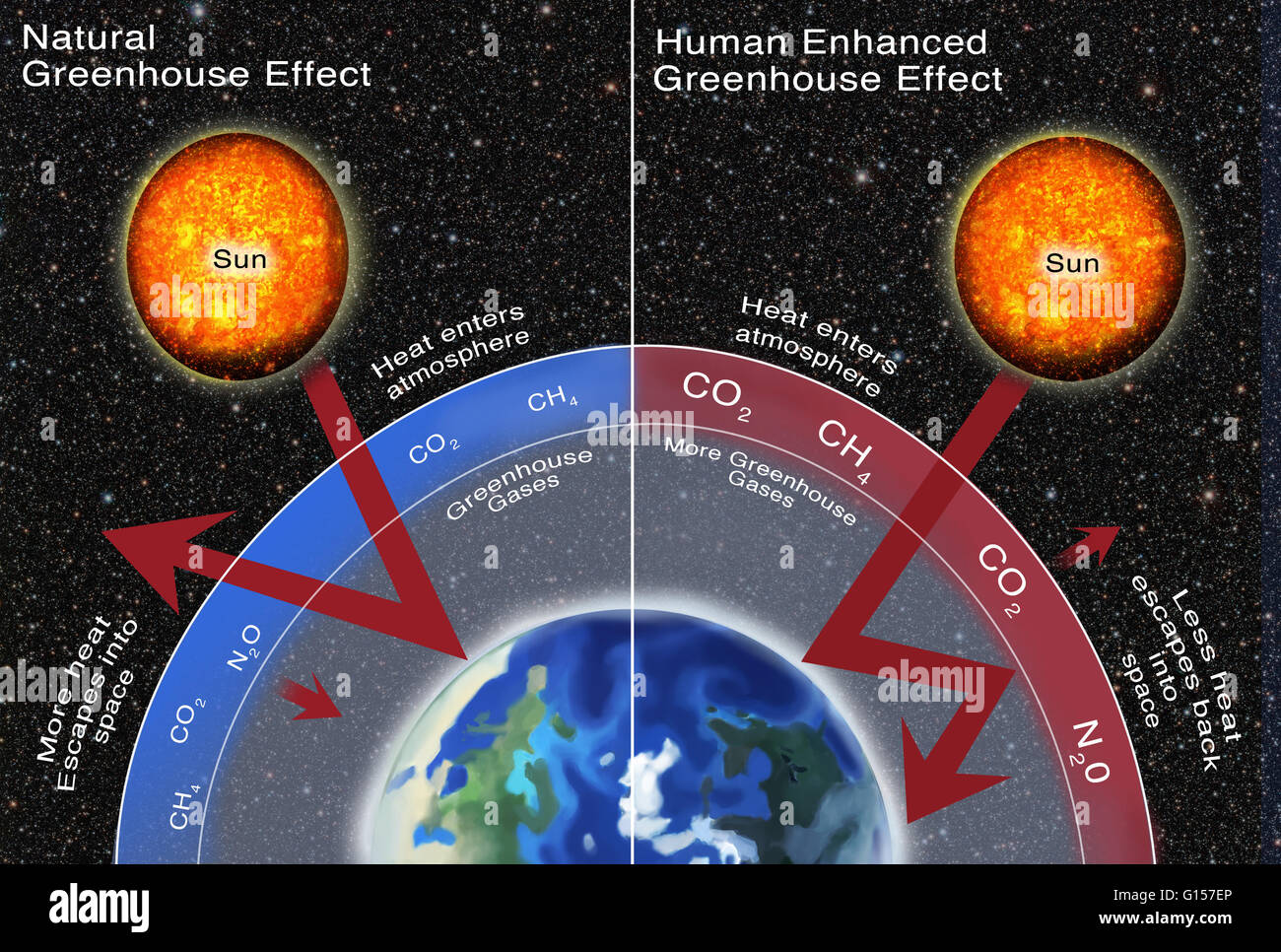



Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy
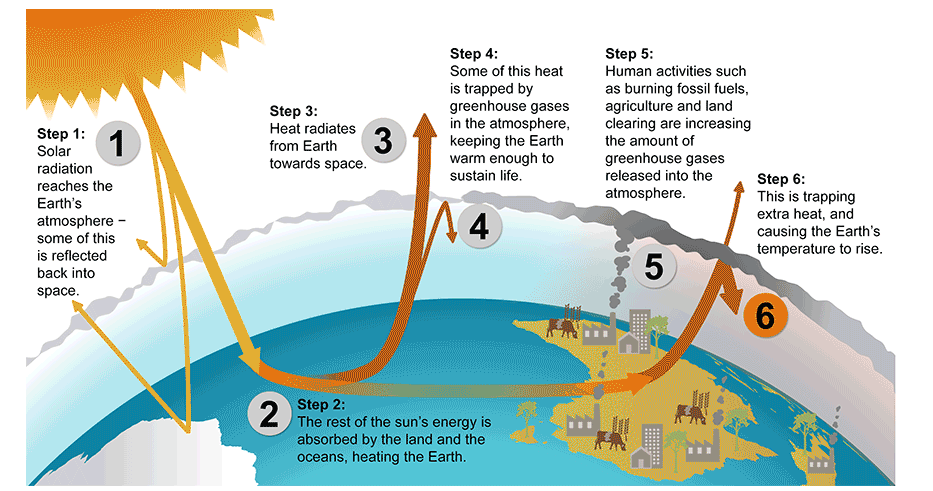



10 4 Global Climate Change Environmental Biology




Global Warming Atmospheric Causes And Effect On Climate Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Lesson 31 Causes Of Global Warming Over



1



1




The Greenhouse Effect Edexcel Igcse Biology Revision Notes



Untitled Document
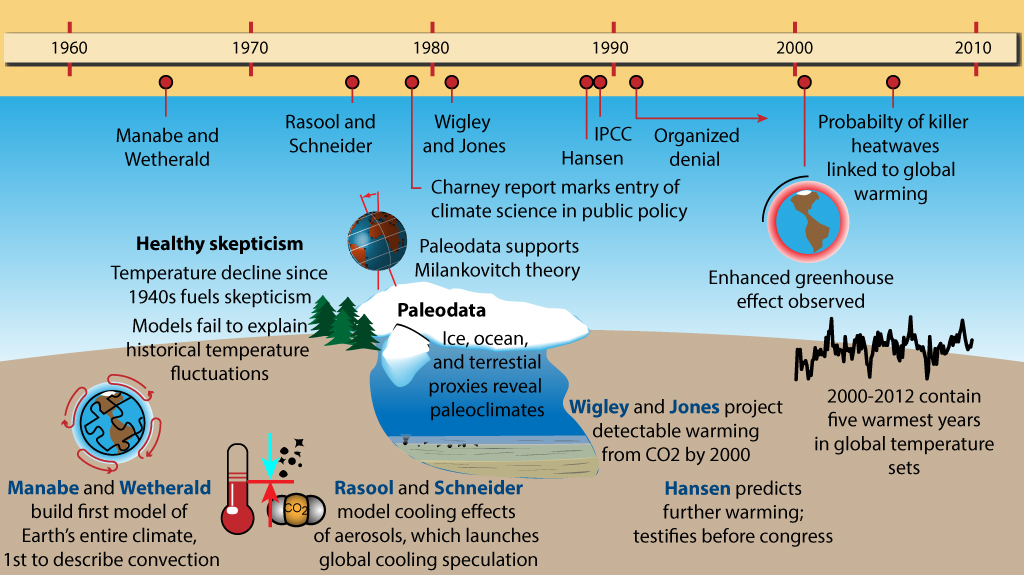



The History Of Climate Science




Natural Greenhouse Effect Human Enhanced Greenhouse Stock Vector Royalty Free



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate
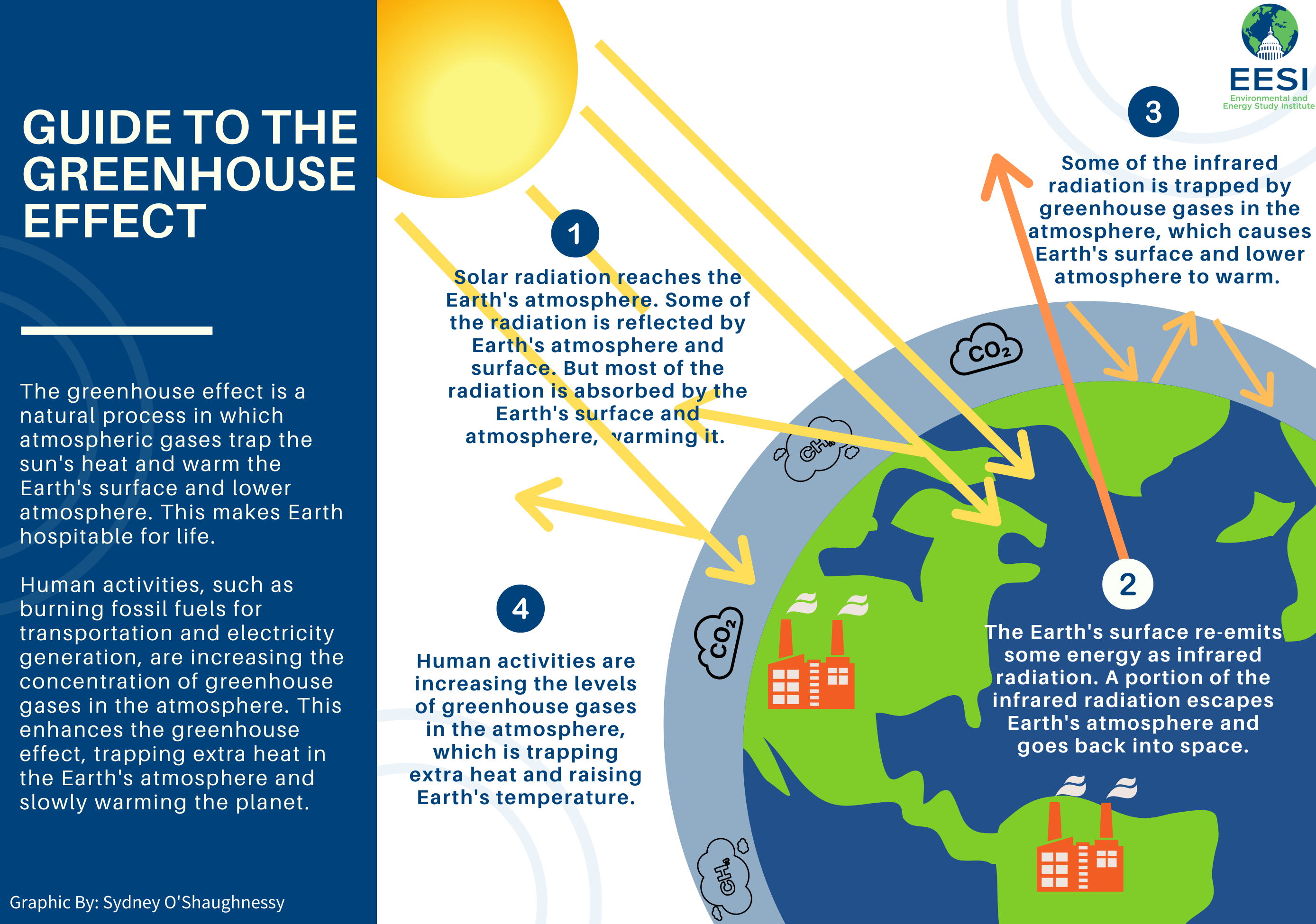



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey
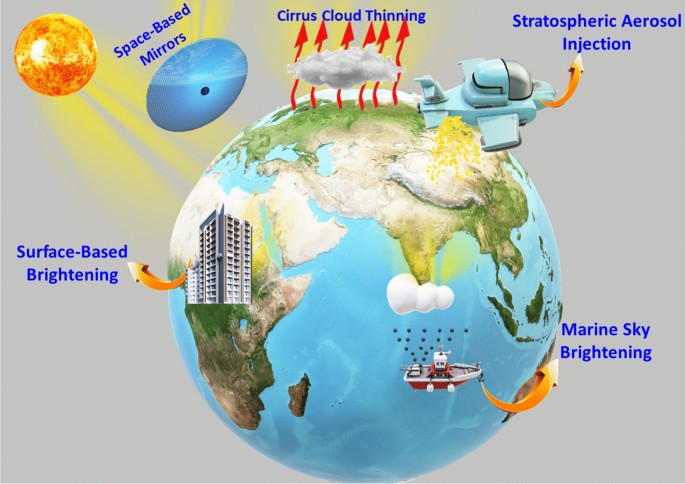



Strategies For Mitigation Of Climate Change A Review Springerlink




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



Untitled Document




Greenhouse Effect Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help



Global Climate Change And The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect



Kids Corner




Global Warming Atmospheric Causes And Effect On Climate Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Difference Between Global Warming And Greenhouse Effect Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet
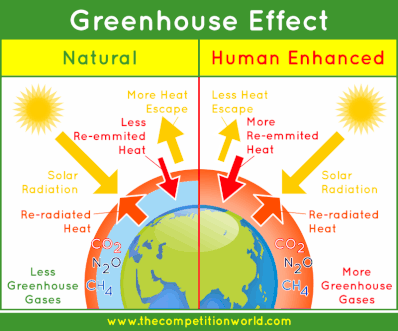



4 4 Climate Change Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green




Human Influence On The Greenhouse Effect Globalchange Gov
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy



Climate Change Ten Year Retreat




Greenhouse Gas An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts



1




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment




The Greenhouse Effect And Causes Of Climate Change




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
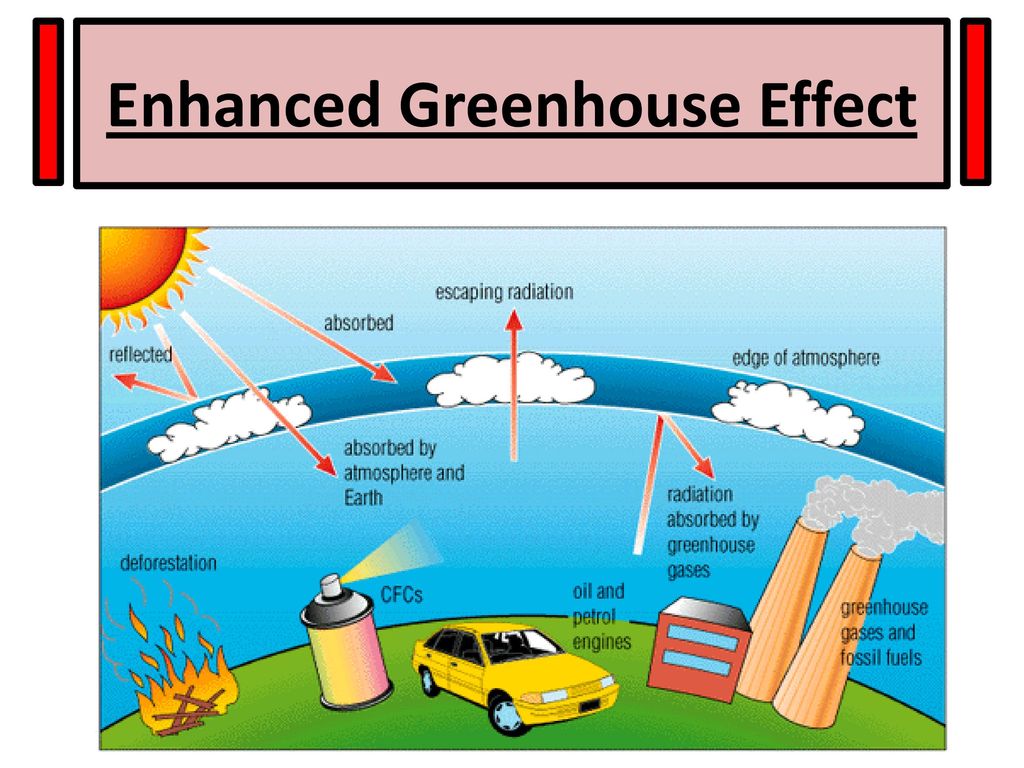



The Causes And Effects Of Climate Change Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Carbon Footprint Of Aluminum Production Emissions And Mitigation Sciencedirect



Untitled Document
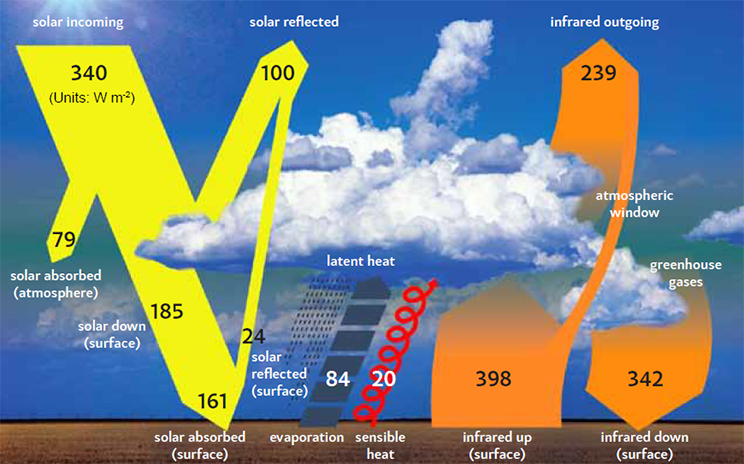



Causes Of Climate Change And Sea Level Rise Coastadapt




The Greenhouse Effect Explained



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa


